Diabetic Foot
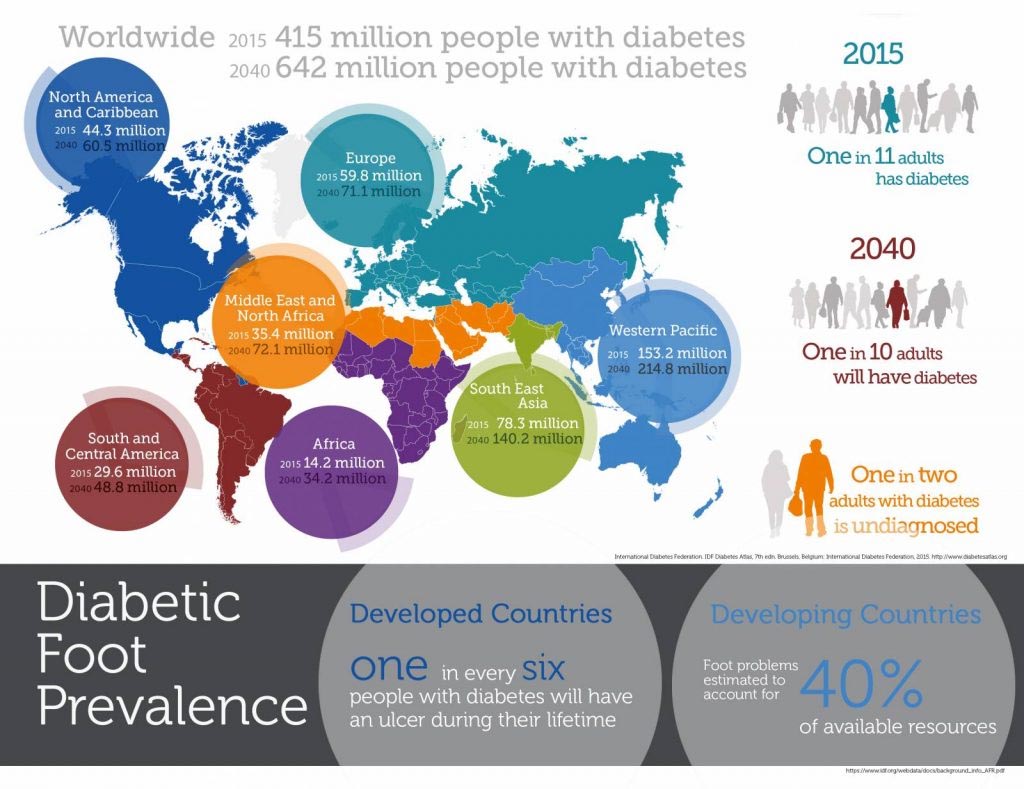
Diabetic foot and lower limb complications are severe and chronic. They affect 40 to 60 million people with diabetes globally. Chronic ulcers and amputations result in a significant reduction in the quality of life and increase the risk of early death.
Less than one-third of physicians recognise the signs of diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy. The resulting missed diagnoses contribute greatly to the high rates of disease and mortality.
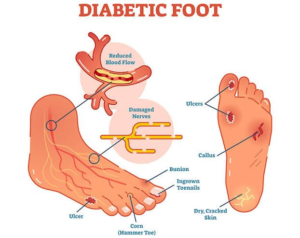
High blood glucose can cause damage to the nerves throughout the body. Neuropathy is a frequently encountered complication of diabetes. Nerve damage can be quite significant and allow injuries to go unnoticed, leading to ulceration, serious infections and in some case amputations.
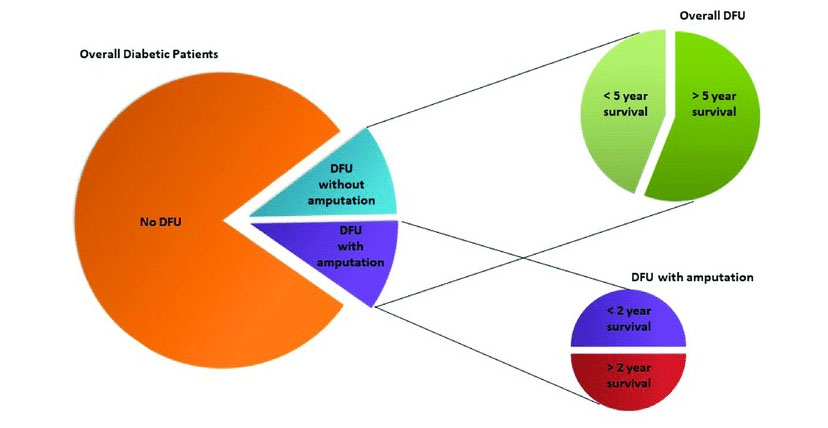
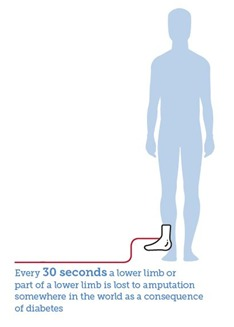
Diabetic foot is one of the most common, costly and severe complications of diabetes. Amputation in people with diabetes is 10 to 20 times more common than in people without diabetes and it is estimated that every 30 seconds a lower limb or part of a lower limb is lost somewhere in the world as a consequence of diabetes.
Diabetic foot and lower limb complications are severe and chronic. They affect 40 to 60 million people with diabetes globally. Chronic ulcers and amputations result in a significant reduction in the quality of life and increase the risk of early death.
Diabetic neuropathy is an impairment of normal activities of the nerves throughout the body and can alter autonomic, motor and sensory functions. Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form of diabetic neuropathy, affecting the outer nerves of the limbs, particularly those of the feet. It mainly alters sensory function, causing abnormal feelings and progressive numbness which facilitates the development of ulcers (diabetic foot).
Diabetic foot is one of the most common, costly and severe complications of diabetes. Amputation in people with diabetes is 10 to 20 times more common than in people without diabetes and it is estimated that every 30 seconds a lower limb or part of a lower limb is lost somewhere in the world as a consequence of diabetes.